Openssl Generate Public Key Pair
- Mar 03, 2020 This page explains how to generate public/private key pairs using OpenSSL command-line tools. Device authentication. Cloud IoT Core uses public key (or asymmetric) authentication: The device uses a private key to sign a JSON Web Token (JWT). The token is passed to Cloud IoT Core as proof of the device's identity.
- $ openssl rsa -pubout -in privatekey.pem -out publickey.pem writing RSA key A new file is created, publickey.pem, with the public key. It is relatively easy to do some cryptographic calculations to calculate the public key from the prime1 and prime2 values in the public key file. However, OpenSSL has already pre-calculated the public key.
OpenSSL provides two command line tools for working with keys suitable for Elliptic Curve (EC) algorithms: openssl ecparam openssl ec The only Elliptic Curve algorithms that OpenSSL currently supports are Elliptic Curve Diffie Hellman (ECDH) for key agreement and Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) for signing/verifying.
Download and install the OpenSSL runtimes. If you are running Windows, grab the Cygwin package.
OpenSSL can generate several kinds of public/private keypairs.RSA is the most common kind of keypair generation.[1]
Other popular ways of generating RSA public key / private key pairs include PuTTYgen and ssh-keygen.[2][3]
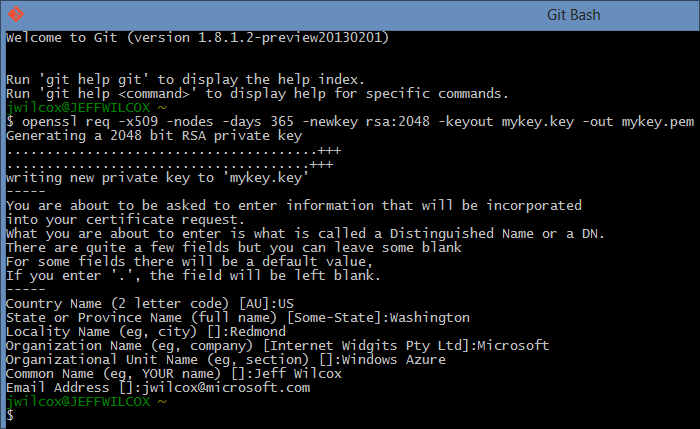
Generate an RSA keypair with a 2048 bit private key[edit]
Execute command: 'openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out private_key.pem -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:2048'[4] (previously “openssl genrsa -out private_key.pem 2048”)
e.g.
Make sure to prevent other users from reading your key by executing chmod go-r private_key.pem afterward.
Extracting the public key from an RSA keypair[edit]
Execute command: 'openssl rsa -pubout -in private_key.pem -out public_key.pem'
e.g.
A new file is created, public_key.pem, with the public key.
It is relatively easy to do some cryptographic calculations to calculate the public key from the prime1 and prime2 values in the public key file.However, OpenSSL has already pre-calculated the public key and stored it in the private key file.So this command doesn't actually do any cryptographic calculation -- it merely copies the public key bytes out of the file and writes the Base64 PEM encoded version of those bytes into the output public key file.[5]
Viewing the key elements[edit]
Execute command: 'openssl rsa -text -in private_key.pem'
All parts of private_key.pem are printed to the screen. This includes the modulus (also referred to as public key and n), public exponent (also referred to as e and exponent; default value is 0x010001), private exponent, and primes used to create keys (prime1, also called p, and prime2, also called q), a few other variables used to perform RSA operations faster, and the Base64 PEM encoded version of all that data.[6](The Base64 PEM encoded version of all that data is identical to the private_key.pem file).
Password-less login[edit]
Often a person will set up an automated backup process that periodically backs up all the content on one 'working' computer onto some other 'backup' computer.
Because that person wants this process to run every night, even if no human is anywhere near either one of these computers, using a 'password-protected' private key won't work -- that person wants the backup to proceed right away, not wait until some human walks by and types in the password to unlock the private key.Many of these people generate 'a private key with no password'.[7]Some of these people, instead, generate a private key with a password,and then somehow type in that password to 'unlock' the private key every time the server reboots so that automated toolscan make use of the password-protected keys.[8][3]
Further reading[edit]
- ↑Key Generation
- ↑Michael Stahnke.'Pro OpenSSH'.p. 247.
- ↑ ab'SourceForge.net Documentation: SSH Key Overview'
- ↑'genpkey(1) - Linux man page'
- ↑'Public – Private key encryption using OpenSSL'
- ↑'OpenSSL 1024 bit RSA Private Key Breakdown'
- ↑'DreamHost: Personal Backup'.
- ↑Troy Johnson.'Using Rsync and SSH: Keys, Validating, and Automation'.
- Internet_Technologies/SSH describes how to use 'ssh-keygen' and 'ssh-copy-id' on your local machine so you can quickly and securely ssh from your local machine to a remote host.
To sign an assembly with a strong name, you must have a public/private key pair. This public and private cryptographic key pair is used during compilation to create a strong-named assembly. You can create a key pair using the Strong Name tool (Sn.exe). Key pair files usually have an .snk extension.
Note
In Visual Studio, the C# and Visual Basic project property pages include a Signing tab that enables you to select existing key files or to generate new key files without using Sn.exe. In Visual C++, you can specify the location of an existing key file in the Advanced property page in the Linker section of the Configuration Properties section of the Property Pages window. The use of the AssemblyKeyFileAttribute attribute to identify key file pairs was made obsolete beginning with Visual Studio 2005.
Create a key pair
To create a key pair, at a command prompt, type the following command:
sn –k <file name>
In this command, file name is the name of the output file containing the key pair.
Openssl Generate Public Private Key Pair
The following example creates a key pair called sgKey.snk.
Openssl Generate Public Private Key Pair And Csr
If you intend to delay sign an assembly and you control the whole key pair (which is unlikely outside test scenarios), you can use the following commands to generate a key pair and then extract the public key from it into a separate file. First, create the key pair:
Next, extract the public key from the key pair and copy it to a separate file:
Once you create the key pair, you must put the file where the strong name signing tools can find it.
When signing an assembly with a strong name, the Assembly Linker (Al.exe) looks for the key file relative to the current directory and to the output directory. When using command-line compilers, you can simply copy the key to the current directory containing your code modules.
If you are using an earlier version of Visual Studio that does not have a Signing tab in the project properties, the recommended key file location is the project directory with the file attribute specified as follows: