Oracle Generate Random Primary Key
- Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Examples
- Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Mean
- Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Definition
- Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Mean
- Oracle Select Primary Key
- Add Primary Key Oracle
Watch out for sequential Oracle GUIDs! (the GUID generator offered by Oracle) was returning sequentially-incremented values, rather than pseudo-random combinations of characters. Never, please never use random Guids as primary key for pretty large database. SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE will be OK, but INSERT will make DBMS to rebuild index. May 25, 2004 Generating random numbers or strings is oft-times a necessity. Oracle provides a random number generator that is faster than writing your won random generation logic in PL/SQL, and can generate both character and alphanumeric strings. Perhaps it is time to learn more about the DBMSRANDOM package. Jan 10, 2020 This article talks how to create table in Oracle,primary key,Foreign keys,create table syntax in oracle with Examples.This will be very useful for Oracle DBA’ s and Developer both.They play with it many times in the day and an good knowledge can definitely help them expedite the task.They often get confused the datatype and what to use in what circumstances. Hello Tom, I have a question on using GUIDs as primary keys. Our application is being developed on 11gR2 with a 3-node RAC. The development team has introduced a new column to almost all of the tables which is technically a UUID generated by the application code.
4 options to generate primary keys. The JPA specification supports 4 different primary key generation strategies which generate the primary key values programmatically or use database features, like auto-incremented columns or sequences. 4 options to generate primary keys. The JPA specification supports 4 different primary key generation strategies which generate the primary key values programmatically or use database features, like auto-incremented columns or sequences.
Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Examples
Date: June 07, 2007 09:22PM
1 do {
2 $random = generate_random_primary_key();
3 mysql_query(check if $random exists in database);
4 if not { insert data row to MySQL, quit loop } // else continue with loop
5 } while $random is in database
However, I have a couple of concerns:
1. Wouldn't this be a little slow and database-intensive, especially when the database already contains a lot of entries as I'll be checking the primary key's existence every time I need to insert an entry? And worse, it'll be inside a loop that continues until a non-existing primary key is found (imagine a 'nearly full' database).
2. I'm concerned about multiple users doing inserts at the same time. How can I be sure that there won't be another user inserting another entry using the same 'random' primary key in between lines 3 and 4?
Any comments would be very much be welcomed!
Content reproduced on this site is the property of the respective copyright holders. It is not reviewed in advance by Oracle and does not necessarily represent the opinion of Oracle or any other party.
The DBMS_RANDOM package provides a built-in random number generator.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Operational notes
Note:
DBMS_RANDOM is not intended for cryptography.Using DBMS_RANDOM
Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Mean
Operational notes
The
RANDOMfunction produces integers in the range [-2^^31, 2^^31).The
VALUEfunction produces numbers in the range [0,1) with 38 digits of precision.
Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Definition
DBMS_RANDOM can be explicitly initialized but does not require initialization before a call to the random number generator. It automatically initializes with the date, user ID, and process ID if no explicit initialization is performed.
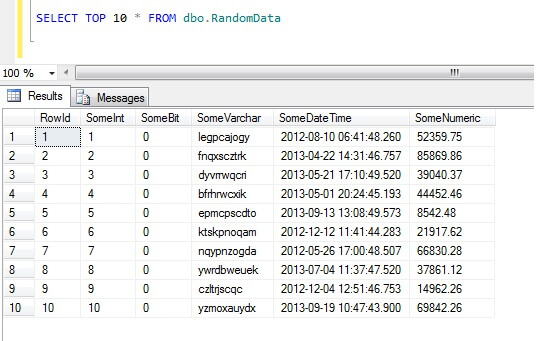
If this package is seeded twice with the same seed, then accessed in the same way, it produces the same result in both cases.
In some cases, such as when testing, you may want the sequence of random numbers to be the same on every run. In that case, you seed the generator with a constant value by calling an overload of SEED. To produce different output for every run, simply omit the seed call. Then the system chooses a suitable seed for you.
Summary of DBMS_RANDOM subprograms
Table 6-1 DBMS_RANDOM package subprograms
| Subprogram | Description |
|---|---|
Initializes the package with a seed value. | |
Returns random numbers in a normal distribution. | |
Generates a random number. | |
Resets the seed. | |
Gets a random string. | |
Terminates package. | |
One version gets a random number greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1, with 38 digits to the right of the decimal point (38-digit precision). The other version gets a random Oracle Database number |
Note:
The INITIALIZE procedure, RANDOM function and TERMINATE procedure are deprecated. They are included in this release for legacy reasons only.Notes:
The
PLS_INTEGERandBINARY_INTEGERdata types are identical. This document usesBINARY_INTEGERto indicate data types in reference information (such as for table types, record types, subprogram parameters, or subprogram return values), but may use either in discussion and examples.The
INTEGERandNUMBER(38)data types are also identical. This document usesINTEGERthroughout.
INITIALIZE procedure
This procedure is deprecated. Although currently supported, it should not be used. It initializes the random number generator.
Parameters
Table 6-2 INITIALIZE procedure parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Seed number used to generate a random number |
Usage notes
This procedure is obsolete as it simply calls the SEED procedure.
NORMAL function
This function returns random numbers in a standard normal distribution.
Return value
The random number, a NUMBER value
RANDOM function
This procedure is deprecated. Although currently supported, it should not be used. It generates and returns a random number.
Return value
A random BINARY_INTEGER value greater than or equal to -power(2,31) and less than power(2,31)
Usage notes
Oracle Generate Random Primary Key Mean
See the NORMAL function and the VALUE function.
SEED procedure
This procedure resets the seed used in generating a random number.
Parameters
Table 6-3 SEED procedure parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Seed number or string used to generate a random number |
Usage notes
The seed can be a string up to length 2000.
STRING function

This function generates and returns a random string.
Parameters
Table 6-4 STRING function parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| What the returning string looks like:
Otherwise the returning string is in uppercase alpha characters. |
| Length of the returned string |
Return value
A VARCHAR2 value with the random string
TERMINATE procedure
This procedure is deprecated. Although currently supported, it should not be used. It would be called when the user is finished with the package.
VALUE function
One version returns a random number, greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1, with 38 digits to the right of the decimal (38-digit precision). The other version returns a random Oracle Database NUMBER value x, where x is greater than or equal to the specified low value and less than the specified high value.
Parameters
Table 6-5 VALUE function parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower limit of the range in which to generate a random number |
| Upper limit of the range in which to generate a random number |
Oracle Select Primary Key
Add Primary Key Oracle
Return value
A NUMBER value that is the generated random number