Set Up Secret Key Generator
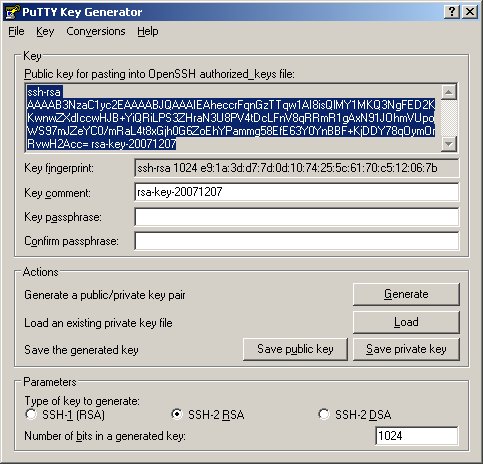
The result of the combination of the 256-bit Rijndael/AES secret key, the unknowable (therefore secret) present value of the 128-bit monotonically incrementing counter, and the 128-bit secret Initialization Vector (IV) is 512-bits of secret data providing extremely high security for the generation of this page's 'perfect passwords'. RandomKeygen is a free mobile-friendly tool that offers randomly generated keys and passwords you can use to secure any application, service or device. KEY RandomKeygen - The. Quickstart: Set and retrieve a secret from Azure Key Vault using the Azure portal.; 2 minutes to read +2; In this article. Azure Key Vault is a cloud service that provides a secure store for secrets. Secret Key Generator for Secure Challenge and Response. Which try all possible combinations of the secret key. This Key Generator, produces an essentially 'random' key, which means one key is a likely as another as far as both you and any attacker can tell. To initialize the key generator, you move your mouse around in the text window. Apr 12, 2018 SSH-key-based authentication provides a more secure alternative to password-based authentication. In this tutorial we'll learn how to set up SSH key-based authentication on an Ubuntu 16.04 installation. Set up public-key authentication using SSH on a Linux or macOS computer; Set up public-key authentication using PuTTY on a Windows 10 or Windows 8.x computer; Before you begin. Using SSH public-key authentication to connect to a remote system is a robust, more secure alternative to logging in with an account password or passphrase. Writing From the Heart. One of the easiest ways to write a terrific story is to write about what you know. You can use prompts below to help you harness your own life and background to come up with story ideas that are easy to develop.
- Managing Kerberos and Other Authentication Services in Oracle® Solaris 11.3
- Document Information
- Using This Documentation
- Chapter 1 Using Pluggable Authentication Modules
- What's New in Authentication in Oracle Solaris 11.3
- About PAM
- Introduction to the PAM Framework
- Benefits of Using PAM
- Planning a Site-Specific PAM Configuration
- Assigning a Per-User PAM Policy
- Configuring PAM
- PAM Configuration Reference
- PAM Configuration Files
- PAM Configuration Search Order
- PAM Configuration File Syntax
- PAM Stacking
- PAM Stacking Example
- PAM Service Modules
- Chapter 2 Kerberos on Oracle Solaris
- What's New in Kerberos in Oracle Solaris 11.3
- Introduction to MIT Kerberos on Oracle Solaris
- Comparison of MIT Kerberos and Oracle Solaris Kerberos
- Differences in Defaults Between MIT Kerberos and Oracle Solaris Kerberos
- Documentation About Kerberos
- Kerberos Documentation
- Oracle Solaris Documentation for Kerberos
- How the Kerberos Service Works
- Initial Authentication: the Ticket-Granting Ticket
- Subsequent Kerberos Authentications
- Kerberos Authentication of Batch Jobs
- Kerberos, DNS, and the Naming Service
- Kerberos and Strong Encryption
- Kerberos and FIPS 140-2 Mode
- Chapter 3 Planning for the Kerberos Service
- Native Oracle Solaris Features Integrated With Kerberos
- Planning KDCs
- Planning for Kerberos Clients
- Using Automatic Installation to Install Kerberos Clients
- Using the kclient Profile to Install Kerberos Clients
- Kerberos Client Login Security
- Trusted Delegated Services in Kerberos
- Planning Kerberos Use of UNIX Names and Credentials
- Automatic User Migration to a Kerberos Realm
- Synchronizing Clocks Between KDCs and Kerberos Clients
- Chapter 4 Configuring the Kerberos Service
- Configuring the Kerberos Service
- Configuring KDC Servers
- Configuring KDC Servers on LDAP Directory Servers
- Configuring a Master KDC on an OpenLDAP Directory Server
- How to Configure a Master KDC on an OpenLDAP Directory Server
- Configuring a Master KDC on an Oracle Unified Directory Server
- How to Configure a Master KDC on an Oracle Unified Directory LDAP Directory Server
- How to Mix Kerberos Principal Attributes in a Non-Kerberos Object Class Type on an OpenLDAP Server
- How to Destroy a Kerberos Realm on an LDAP Directory Server
- Configuring Kerberos Clients
- Configuring Kerberos Network Application Servers
- Configuring Kerberos NFS Servers
- Configuring Delayed Execution for Access to Kerberos Services
- How to Configure a cron Host for Access to Kerberos Services
- Administering the Kerberos Database
- How to Convert a Kerberos Database After a Server Upgrade
- Observing Mapping From GSS Credentials to UNIX Credentials
- Increasing Security on Kerberos Servers
- Restricting Access to KDC Servers
- Using a Dictionary File to Increase Password Security
- Chapter 5 Users Using Kerberos
- Kerberos Password and Ticket Management
- Administrative Responsibilities for Kerberos Password and Ticket Management
- User Responsibilities for Kerberos Ticket Management
- User Responsibilities for Kerberos Password Management
- User Remote Logins in Kerberos
- Chapter 6 Using Simple Authentication and Security Layer
- About SASL
- SASL Reference
- SASL Plugins
- SASL Environment Variable
- SASL Options
- Chapter 7 Using Smart Cards for Multifactor Authentication in Oracle Solaris
- Two-Factor Authentication and Smart Cards
- About Two-Factor Authentication
- Implementation of Two-Factor Authentication in Oracle Solaris
- Software Cryptographic Providers for Smart Cards
- Hardware Readers for Smart Cards
- Smart Card Architecture in Oracle Solaris
- Configuring an Oracle Solaris System for Smart Card Login
- Main Smart Card Configuration Tasks
- Installing Smart Card Packages
- How to Install the Smart Card Packages
- Using pcsclite for Smart Cards
- Configuring libccid for Smart Card Readers
- How to Configure and Debug libccid
- Configuring a Desktop for Users With Smart Cards
- Configuring OCSP Certificates for Smart Cards
- How to Configure and Validate Certificates
- Configuring PAM for Smart Cards
- Configuring Secure Shell Clients for Smart Cards
- How to Configure the Secure Shell Client for Smart Cards
- Enabling an Oracle Solaris System for Smart Card Login
- How to Enable Smart Card Authentication
- Enabling Your Web Browser and Email to Use Your Smart Card
- Using a Smart Card
- Chapter 8 Using One-Time Passwords for Multifactor Authentication in Oracle Solaris
- About OTP in Oracle Solaris
- OTP Administration in Oracle Solaris
- Configuring and Using OTP in Oracle Solaris
- Chapter 9 Configuring Network Services Authentication
- About Secure RPC
- NFS Services and Secure RPC
- Kerberos Authentication
- DES Encryption With Secure NFS
- Diffie-Hellman Authentication and Secure RPC
- Administering Authentication With Secure RPC
- Authentication Services Glossary
- Index
Please follow the below steps to setup Amazon – S3 in XFilesPro.
Step 1:
Login to Amazon S3 – https://aws.amazon.com/s3/
If you have not registered, you can register using the Signup option.
Step 2:
After successful login, you will receive the below screen –
Step 3:
Click on S3 under Storage. You will receive the below screen –
Step 4:
Click on “Create Bucket” and enter Bucket Name, Region & Copy Settings from an existing bucket details as shown in the below screenshot –
Step 5: After entering Bucket Name and Region,click on Create button.This bucket creation is similar to a new folder creation on your computer. All your files will go into this bucket(folder).
Step 6:
After creating the bucket, click on the name of the bucket.

When the bucket details open up, click on Permissions tab.
Under Manage Public Permissions,click on Everyone.
Check all the boxes under Object Access & Permissions Access and click SAVE
You will receive the below screen –
Step 7:
Click on the “Add CORS Configuration” under Permissions.
You will see a set of codes under CORS configuration editor.
Change the parameters inside the Editor to the following and press SAVE and CLOSE:
Step 8:
After saving the code in CORS Configuration Editor, click on your profile name – My Security Credentials then click on Continue to Security Credentials button.
Step 9:
Expand the Access Keys (Access Key ID and Secret Access Key) option.
You will see the list of your active and deleted access keys.
Secret Key Indonesia
- To generate new access keys, click the Create New Access Key button.
- After clicking the Create new access key button the screen will appear like the following.
- Click Show Access Key to have it displayed on the screen. Note, that you can download it to your machine as a file and open it whenever needed. To download it, just click the Download Key File button.
Attention! If you do not write down the key or download the key file to your computer before you press “Close” or “Cancel” you will not be able to retrieve the secret key in future. Then you’ll have to delete the keys which you created and start to create new keys.
Keep a note of this key details as it is required for setting up the XfilesPro app
Access Key ID
Secret Access Key
Set Up Secret Key Generator Reviews
Please keep access key and secret key handy when you are configuring S3 as your external storage. Know more on how to configure S3 as your external storage with the help of this access key and secret key.